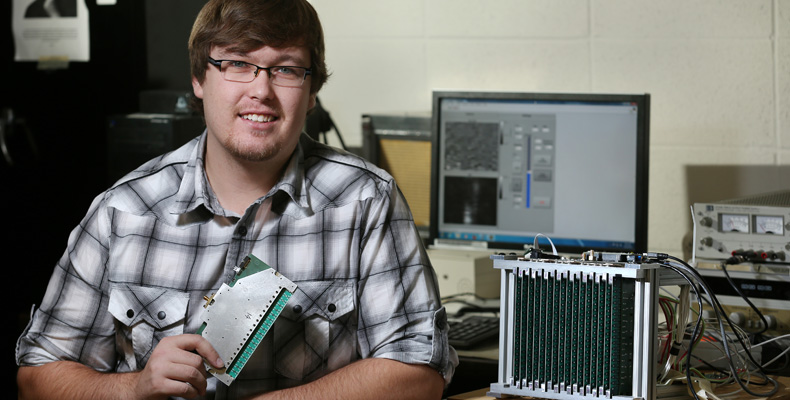

Matt Horst won a spot in the coveted 2015 National Science Foundation (NSF) Graduate Research Fellowship Program for his work in developing a 3-D real-time wideband microwave camera that can produce images. Sam O’Keefe/Missouri S&T
At 7 a.m. on a weekday, many college students are still asleep. Others hit the snooze button and struggle to get out of bed for an 8 a.m. class. But not Matt Horst. He is usually already at work in the Applied Microwave Nondestructive Testing Laboratory (AMNTL) at Missouri S&T.
Horst, a graduate student pursuing a master’s degree in electrical and computer engineering at S&T, spends most of his time working in the lab running simulations, fabricating circuit boards or reading literature related to his research.
The winner of a coveted spot in the 2015 National Science Foundation (NSF) Graduate Research Fellowship Program, Horst is working to develop a 3-D real-time wideband microwave camera that can produce images. [Read more…]









Recent Comments